Electron Microscopy of bronchoalveolar lavage of severe COVID-19 patients
- Abstract number
- 111
- Presentation Form
- Poster & Flash Talk
- DOI
- 10.22443/rms.mmc2023.111
- Corresponding Email
- [email protected]
- Session
- Public Health: The Impact of Microscopy
- Authors
- Ms Shikha Chaudhary (1), Dr Subhash Chandra Yadav (1)
- Affiliations
-
1. Electron Microscopy Facility, Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi, India
- Keywords
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS- CoV-2); cellular infectivity and ultrastructural changes; bronchoalveolar fluid (BALF);
- Abstract text
We examined the cellular infectivity and ultrastructural changes due to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS- CoV-2) infection in the various cells of bronchoalveolar fluid (BALF) from intubated patients of different age groups (≥60 years and <60 years) and with common comorbidities such as diabetes, liver and kidney diseases, and malignancies. BALF of 79 patients (38 cases >60 and 41 cases <60 years) were studied by light microscopy, immunofluorescence, scanning, and transmission electron microscopy to evaluate the ultrastructural changes in the ciliated epithelium, type II pneumocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, and enucleated granulocytes. This study demonstrated a relatively greater infection and better preservation of subcellular structures in these cells from BALF of younger patients (<60 years compared with the older patients (≥60 years). The different cells of BALF from the patients without comorbidities showed higher viral load compared with the patients with comorbidities. Diabetic patients showed maximum ultrastructural damage in BALF cells in the comorbid group. This study highlights the comparative effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the different airway and inflammatory cells of BALF at the subcellular levels among older and younger patients and in patients with comorbid conditions.
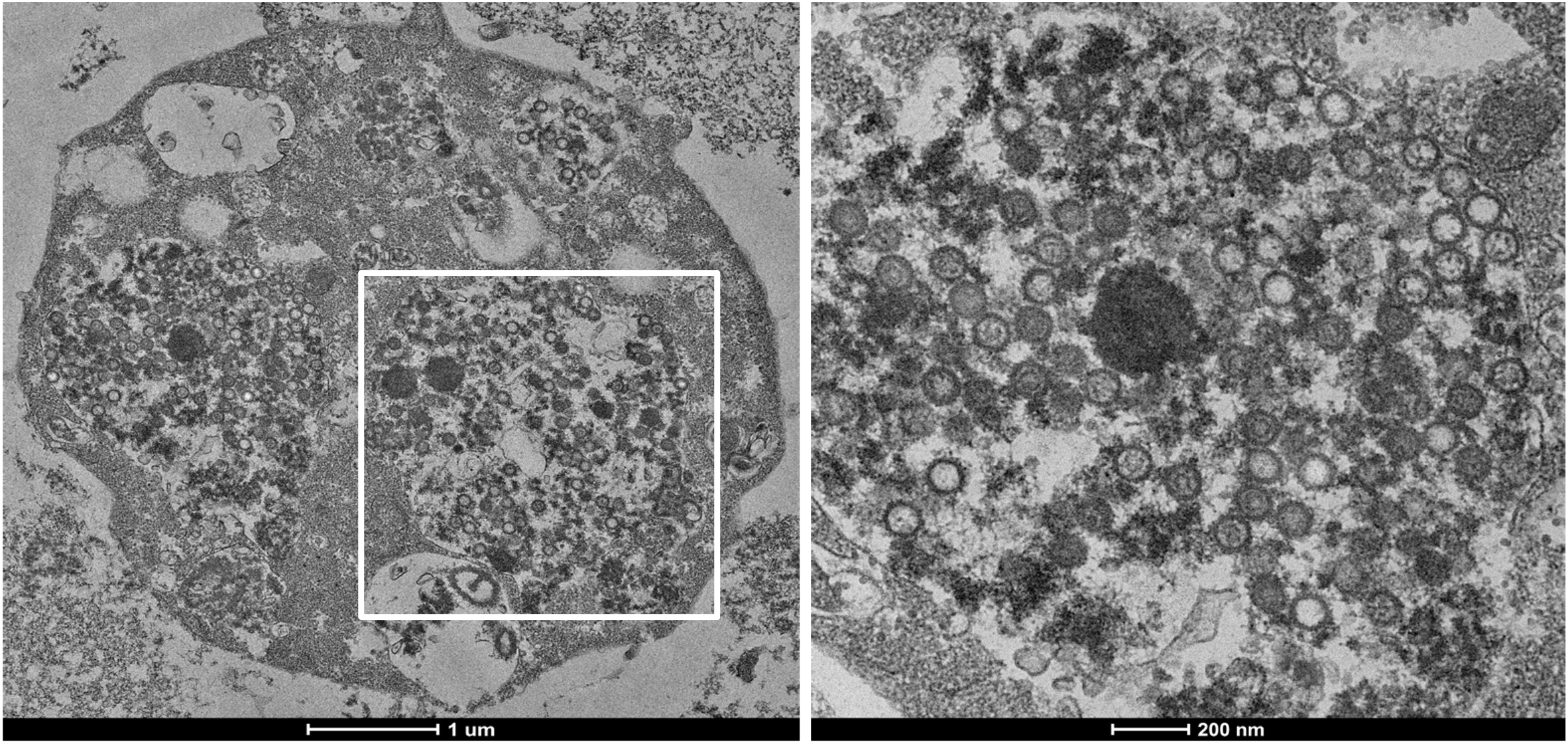
Figure: Transmission Electron Microscope imaging of enucleated Granulocytes with phagocytosed matured SARS-CoV-2 from the BALF of the intubated ARDS COVID-19 positive patient.
- References
1. Shikha Chaudhary, Preeti Rai, Arti Joshi, Pooja Yadav, Kishore Sesham, Shailendra Kumar, Asit Ranjan Mridha, Upendra Baitha, Tapas Chandra Nag, Kapil Soni, Anjan Trikha, Subhash Chandra Yadav*: Ultracellular imaging of bronchoalveolar lavage from young age COVID-19 patients with comorbidities showed greater SARS-CoV-2 infection but lesser ultrastructural damage than the old age patients. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 2022 Sep 6;1-25.
2. Shikha Chaudhary, Preeti Rai, Kishore Sesham, Shailendra Kumar, Prabhakar Singh, Tapas Chandra Nag, Pratima Chaudhuri, Anjan Trikha & Subhash Chandra Yadav*: Microscopic imaging of bronchoalveolar fluids of COVID-19 positive intubated patients reveals the different level of SARS-CoV-2 infection on oral squamosal epithelial cells. Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics Vol.58, June 2021, pp. 196-207.