New developments on chameleon: multihole grids as a screening tool and modified grid surfaces
- Abstract number
- 312
- Presentation Form
- Poster & Flash Talk
- DOI
- 10.22443/rms.mmc2023.312
- Corresponding Email
- [email protected]
- Session
- Cryo-Electron Microscopy
- Authors
- Miriam Weckener (2), Ivan Fong (2), Paul Thaw (2), Daniel Clare (1), Michele Darrow (2)
- Affiliations
-
1. Diamond Light Source
2. SPT Labtech
- Keywords
cryo-electron microscopy, sample preparation, blot-free technology, grid modification
- Abstract text
The chameleon® system automates the sample preparation workflow for single-particle cryo-EM and utilises blot-free technology with nanowire grids. In this poster, we will describe the expansion of our nanowire grid range, highlighting new developments including graphene oxide modified grids and our new multihole grids.
Modifying grids with a continuous layer of carbon, graphene or graphene oxide has been shown to help with issues such as orientation bias, as well as particle distribution and denaturation at the air-water interface. We show it is possible to apply a graphene oxide layer to Quantifoil® Active grids for chameleon and the effects this has on the grid preparation workflow. A range of samples was used to analyse what effects the addition of graphene oxide to Quantifoil Active sample supports has on particle orientation and distribution, and the obtainable resolution.
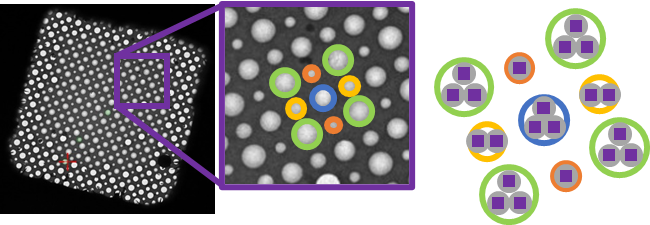
Quantifoil Active multihole grids are made of a copper mesh with self-wicking nanowires and either a holey carbon or gold support film. They contain four different hole sizes on each grid square, arranged in a regular pattern (Figure 1). They are an ideal screening tool to identify a sample’s preference for a specific film geometry. Proteins of various sample types and shapes were tested to study the effect of hole size and spacing on particle distribution and orientation.
Figure 1. TEM image of a Quantifoil Active multihole grid square. The inset shows a close-up of an area in the gridsquare to highlight the four different hole sizes. The arrangement of image acquisition areas used for high-magnification imaging is shown on the right.